Introduction: In recent years, wind energy has developed around the world to offer a more sustainable alternative to electricity production. Taking the United States as an example, the total annual wind energy production varies from2000annual60billion kilowatt hours have gone to2021meeting of the year3800Billions of kilowatt hours. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), which represents approximately 10% of total utility-scale electricity generation in the United States.9.2%. There are still many challenges ahead, but progress deserves recognition. Among these issues, some customers believe that wind turbines cannot be built unconditionally while taking into account the recyclability of the blades produced.

It is reported thatBelgianGarbage in the windThe association was created to meet these challenges. The company uses additive manufacturing technologies, primarily fused deposition models (FDM), using recycled plastic to design wind turbines. non-profit organizationGarbage in the windfounder ofBramPreviously, he had carried out research on the environmental impact of large wind turbines within the Flemish government and gained valuable experience. Today, through his own company, he promotes open source software to the public.3DWind turbine printing is a more environmentally friendly way to use energy.Garbage in the windreceived an international award and additional support from the Antwerp Climate Fund in Belgium.

△BramPeirssocket3DPrinted wind turbine blades
Garbage in the windcontext of the establishment
While working for the Flemish government,BramNote that there is still a lot of resistance to the deployment of wind turbines. Even though there are already fairly strict rules to limit the environmental impact of wind turbines, people are not aware of them. They worry that wind turbines will cause noise pollution and block their view, which is why they don’t want them in their gardens. To get people to look at wind energy in a different light,BramHe began trying to make wind turbines from old barrels and magnets from old hard drives, and met like-minded partners on the Internet.
Bramnow withCircus of timeCollaboration, a non-profit group that makes all sorts of things from recycled materials, they also operate in BelgiumHangar 21AndPanic at the bar。TimeCircusThe first homemade wind turbine blades were manufactured byPVCMade from sewer pipes, its UV resistance is not strong, and the blades have been damaged, causing power generation failure. final,Bramit took200Euro purchased a printer using3DPrint the repaired slides.

△Source of photos:Garbage in the wind
Printing with plastic is sometimes not as easy as it seems, it can shrink and warp,BramIt took months to achieve this. later,BramPrinted yet another completely custom wind turbine measurement20x20x20centimeter. This wind turbine has been working well for several months and it ensuresBramexistHackaday(an international platform for innovative creators) won10000A bonus in dollars, which is a big incentive for them.
Remove barriers to renewable energy, particularly small-scale wind energy, and bring energy production closer to populations,BramCreatedGarbage in the windassociation. The company’s current business model relies primarily on research and outreach, which it does through bonuses and grants. Additionally, they received funding from the City of Antwerp Climate Fund, which is a great encouragement for the company’s public welfare goals.

△ByrPETProduction of a wind turbine prototype. Photo credit:Garbage in the wind
3DPrint durability
Recycling wind turbine blades has always been a big problem when they20When the service life is reached after 10 years, the fiber and resin can no longer be separated. The only thing you can do is grind them up and put them in a landfill or reuse them in asphalt. In the United States, they are often buried in landfills.
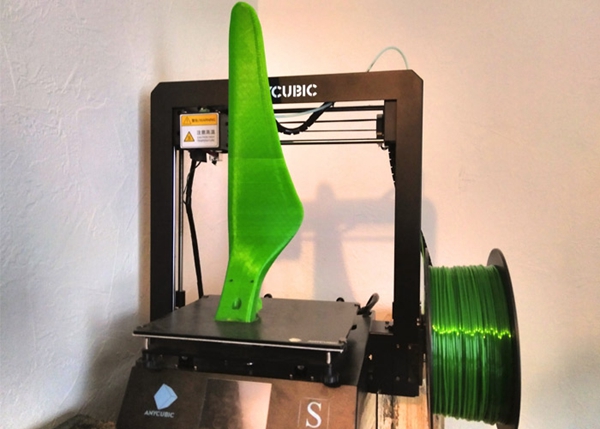
Pure plastic blades are fully recyclable, unlike fiberglass reinforced blades used by other manufacturers.BramReinforced plastics without added fibers are deliberately chosen for printing. Because with current recycling methods, plastic is still “polluted“the potential for reuse is much lower. Today, a lot of plastic waste is generated during the printing process, so the origin of this material is unclear. For example,PLABiomaterials can be produced somewhere and then transported to another industrial facility where they are transformed into long filaments. It isBramChoose to userPETwhy it is recycledPETMade of, which is the plastic used in plastic bottles. Either way, it needs to be recycled, and it’s already available locally, and it contains morePLABetter mechanical properties.
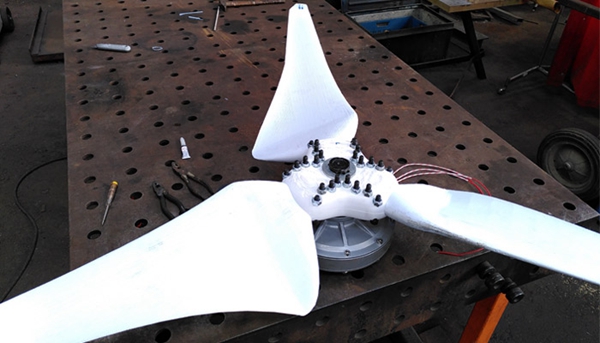
△Source of photos:Garbage in the wind
Garbage in the windfuture projects
Garbage in the windThere are plans to build even larger wind turbines, with lengths of up to4meters, which would produce what an average household would need50%energy, complementary to the production of photovoltaic energy. They also plan to connect all wind turbines to computers so that the consumer can see at any time how much energy their turbine is producing, as well as safety parameters such as vibration. at present,Garbage in the winddevelop their ownMPPTcontroller, which will be completely open source.

△Source of photos:Garbage in the wind
source:
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















