ABS and PLA are currently commonly used plastic materials for 3D printing, but for customers who are new to 3D printing, they don’t know how to choose the right material for them. This article will analyze the similarities and differences between PLA and ABS in terms of performance versus printing requirements, in hopes of helping everyone better understand their usage.
1. Characteristics and performance of PLA and ABS
When talking about the properties of PLA versus ABS, the first thing to consider is what they are made of. Although both are thermoplastics, there are differences. PLA is known to be made from organic sources such as corn or sugarcane, while ABS, like most standard plastics, is made from petroleum. Specifically, PLA is made from fermented plant starch from sources such as corn, cassava, maize, sugar cane or sugar beet pulp, where the sugars are converted into lactic acid, which is then polymerized into polylactic acid. In contrast, ABS is composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene. Acrylonitrile is a synthetic (artificial) monomer derived from propylene and ammonia, butadiene is a petroleum hydrocarbon, and styrene is made by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene (removal of hydrogen through a chemical reaction). These materials have an impact on environmental “sustainability”.

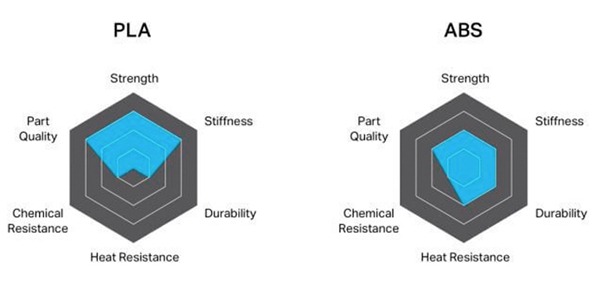
△As shown in the image above (image source: Fictiv), there are differences in appearance and performance between PLA and ABS 3D printed parts.
PLA is often presented as a more ecological material because it is biodegradable. However, it is important to note that it only truly biodegrades under the right conditions, and many cities do not have the adequate tools to properly degrade this material. This means that while it is possible, it is actually only truly “green” through industrial composting. ABS, on the other hand, is considered an unsustainable or environmentally friendly material. As we mentioned, like most plastics, it is made from petroleum, which means its processing is not sustainable. However, one advantage is that ABS is recyclable, and many people don’t realize how limited the biodegradability of PLA is. Some beginners can therefore be more confident that the PLA will be disposed of properly without creating more waste.
Difference 1: ABS has better heat resistance and mechanical properties
Beyond the roots of the material, ABS and PLA also have another different characteristic:heat resistance. ABS has some heat resistance and a high glass transition temperature, while PLA melts at much lower temperatures and is therefore considered non-heat resistant. This will of course affect the application of the material, which will be presented in detail later.
If you are looking for aMore resistant and has better mechanical propertiesAs a material, the author recommends that you use ABS. In addition to being heat resistant and having higher thermal deformation, it is also more durable than PLA.Impact resistant, more durable and lighter. But both materials have similar tensile strengths (ABS is slightly lower), with ABS generally being more suitable for more industrial applications, mainly due to its improved ductility and ability not to break, as well as its higher bending strength and elongation before break. Due to these various properties, ABS can even be used for end-use applications, which is one of the reasons why it is so popular in industries such as injection molding.
△Characteristics of PLA and ABS
It should be noted that PLA is more durable than ABS.Getting stronger and harder. However, as its melting point is very low, it will lose these properties above 50 degrees Celsius and therefore cannot be used in environments involving higher temperatures. However, although ABS is significantly more heat resistant than PLA, as both are thermoplastics, they will degrade over time from UV rays and high temperatures.
Difference 2: PLA is easier to print
Now that we have introduced the characteristics of PLA and ABS, the next step is to discuss the 3D printing process itself. First, because the glass transition temperatures of the two thermoplastics are different, the print preparation will be different. Indeed, the temperature range in which the thermodynamic transformations of substances occur must be taken into account. For PLA, the glass transition temperature range is between 60 and 100°C, while for ABS it is between 105 and 200°C. This determines the parameters defined in the slicer and the time necessary to heat the 3D printer and reach the desired temperature.
At the same time, variables in the manufacturing process, including the print platform and print head, must be correctly configured. ABS requires a higher print bed temperature, around 80-110°C, while PLA is typically 60°C. In terms of extruders, PLA also requires lower temperatures, notably around 180-230°C, while ABS requires 210-250°C.
In terms of ease of use, ABS is known to be more complex to print than PLA. Printing issues encountered are also related to temperature and the properties of each material. PLA has a lower melting temperature than ABS, so when the part 3D printing process is complete, the thermal changes as the layers cure are lower. However, because ABS requires higher temperatures to melt, there will be more abrupt changes as the part cools. This thermal shrinkage can lead to deformation of the parts. One of the most common problems is warping, when the ends of the part shrink, pull away from the pallet and become distorted. To avoid this, when printing with ABS, it is crucial to control the temperature and printing environment, and use adhesive if necessary.
△ABS is prone to warping, a problem related to the material shrinking during sudden temperature changes.
Both materials print at approximately the same speed, eliminating the need to readjust speed settings in the slicer for different materials. PLA is typically printed at 60mm/sec, with some users using even higher speeds. On the other hand, ABS is usually in the 40-60mm/s range and struggles to reach higher speeds.
Another point to keep in mind during the manufacturing process is the waste emissions generated during the manufacturing process, as almost all thermoplastic filaments can produce harmful odors and gases during the printing process. When a material is heated, it releases substances containing particles harmful to health. As for PLA, since it comes from natural plant sources, it does not have a strong odor, so there is nothing to worry about. However, ABS can emit toxic fumes and unpleasant odors, and I highly recommend using an enclosed print case and air filter when using ABS to prevent fumes from being released in the workspace. Nevertheless, constant ventilation is recommended during the printing process to ensure that fumes do not reach our lungs. This is due to the presence of styrene in ABS, a material toxic to humans when inhaled.
Luke Taylor, Marketing Manager at Polymaker explains: “ PLA is a more fragile material, but its advantage is that it is easy to work with and print.Users do not need a heated bed or high temperature, and its shrinkage rate is very low, while the shrinkage rate of ABS is very high. Generally speaking, we see that the better the mechanical properties, the more difficult it is to use. Although we can also add something to PLA to make it stronger without changing the adaptability of the print. “
△Digital 3D printing using Polymaker PLA filament (Photo source: Polymaker)
Difference 3: post-processing
Most post-processing techniques are available for both thermoplastics. There are, however, some notable differences, such as the finish of the parts after printing. PLA parts tend to have a glossier finish, while ABS parts tend to have a more matte finish. Both materials can also be painted for decoration after printing.ABS is generally easier to reprocess than PLA. First, while both can be sanded, the process is easier due to the durability of ABS. PLA is also more difficult to sand because it has low heat resistance and melts more easily.
At the same time, not only is ABS easier to post-process using these basic methods, but if you want a truly glossy finish, ABS parts can be smoothed with acetone vapor. Acetone is a colorless liquid commonly used as a solvent for plastics. Although it won’t work with PLA, those with ABS parts can use acetone for faster post-processing and glossy finishes. A similar process can still be done with PLA. If you want to steam smooth parts made from PLA filament, THF or Tetrahydrofuran can be used for manual polishing.
△These finished pieces have a shiny surface thanks to acetone smoothing (Photo source: zortrax)
Difference 4: PLA has a lower price
The current price of PLA on Mohou.com is 0.65 yuan per gram, and the price of domestic ABS is 1.99 yuan per gram. Relatively speaking, ABS is more expensive than PLA. However, the price also depends on the performance, and it depends on the material you want to choose.
2. Application of PLA and ABS
Another major difference we can find when discussing PLA and ABS is the application areas in which each material is used. PLA is the most commonly used material in FDM 3D printing and is primarily used in manufacturing environments. This is mainly due to its ease of printing, as well as its fragile nature, fragile and sensitive to sunlight and heat. For this reason, it is often widely used by novice users or to create decorative pieces and toys.
ABS, on the other hand, is a more industrial material with advanced properties that, although more difficult to print, allow for higher quality parts. This is why it is often used in the development of prototypes, gears or tools. In short, it is generally implemented in situations where parts may be subjected to physical stress and high mechanical and thermal resistance is required. Therefore, before starting the additive manufacturing process, evaluate the differences between the two materials to create parts based on their intended use.
△PLA is commonly used in more manufacturing applications, decorative items and toys. ABS can be used in applications requiring higher mechanical and thermal resistance.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.