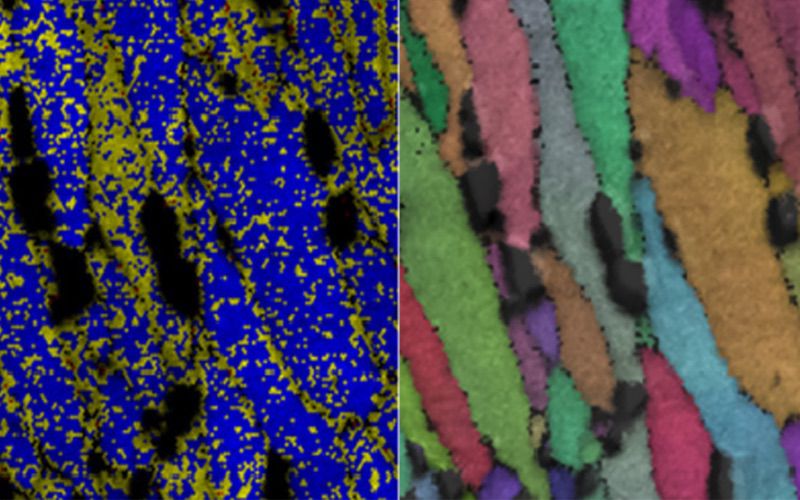
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) have discovered a mechanism called “charge rearrangement” in 3D printed alloys that could enable the design of lightweight materials with better performance for vehicles. Acta Materialia magazine.
Image source: ORNL
One way to improve vehicle fuel efficiency is to use aluminum-based materials to make vehicles lighter. Researchers monitored one of ORNL’s ACMZ (aluminum, copper, manganese, and zirconium) alloys as the material deformed when subjected to sustained mechanical stress at elevated temperatures.
Using neutron diffraction, the researchers studied the atomic structure of the material and observed that the overall stress was absorbed in one part of the alloy but transferred to another part during deformation. This back and forth prevents the strengthening of certain areas.
Researchers such as Michi said that even if the volume fraction reaches almost 10%, θ-Al2Cu, the main strengthening phase of the alloy, still fails to strengthen the load transfer during creep deformation. . In contrast, the evolution of lattice deformation proposes a new mechanism called “charge rearrangement”, in which the initial charge is transferred along grain boundaries from the precipitate-free region, while most θ- particles Al2Cu are located inside the grains strengthened by precipitation.
Despite the absence of load transfer strengthening, the fabricated AM Al-Cu-Mn-Zr alloy still exhibits higher creep resistance at 300 °C than cast alloys of similar compositions. The proposed charge distribution mechanism explains the lack of reinforcement observed in L12-Al3Zr at 300 °C and allows the identification of several strategies to improve the high-temperature mechanical response of AM aluminum alloys.
“Neutrons provide the opportunity to study metallurgical phenomena in multiphase structural materials,” said ORNL researcher Amit Shyam. “Our new advances in high-temperature materials research will enable the design of improved aluminum alloys suitable for extreme conditions.”
Source: 3D Printing Network
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.