High-resolution 3D printer (1): The ultimate guide
High Resolution 3D Printer (2): Highest resolution FDM 3D printer

Large format printingUltra-fine product details-Sonic Mega 8K made easy
Resin 3D printers come in different technology subtypes, but all work by selectively curing a UV-sensitive liquid polymer one layer at a time. Since the resin is cured horizontally and the layer slices are then raised vertically (or lowered vertically, depending on the printer), the technology can occur simultaneouslyXY and Z measurements.
You may be familiar with two-dimensionalXY measurements, such as the pixel resolution of a cell phone screen. In 3D printing, pixels or 3D pixels with height are called voxels.
Voxel resolution measurements for3D printers are less common because the horizontal resolution of a resin 3D printer can be lower than the vertical resolution. As a result, most resin 3D printer manufacturers promote horizontal (XY) as the resolution benchmark for their machines, such as the “51 micron XY resolution” on the Elegoo Jupiter 6K, sometimes also offering Z resolution. .
In fact, the resinThe Z resolution of a 3D printer is difficult to measure unambiguously. Most resin 3D printer manufacturers indicate layer height (Z) values between 1 and 10 microns on their technical sheets. This means that their Z-axis stepper motors (the mechanical parts that control the build plate) can achieve these dimensional steps. Resin machines are capable of producing these small layers, both in theory and in practice on specialized machines. However, the biggest impact on Z resolution is actually how the light source and machine settings work together.
To create these thin layer details, your resin must absorb and block just the right amount of light to cure one layer, but not cure so deeply that it affects multiple layers. If the healing is too deep, you may have“Full cure” or bleed, and your current coat will still be exposed and cured in parts of the previous coat. Therefore, achieving small and reliable Z resolution requires good resin (preferably slow resin), a perfectly matched setup, a tip-shaped light source, and the precision of the on-axis stepper motor. Z.
Finally, pixel size is an easier metric to measure and communicate, so it becomes the default for resolution.
Here we look at the three most common resin or reductive polymerization techniques:LCD, DLP and SLA.
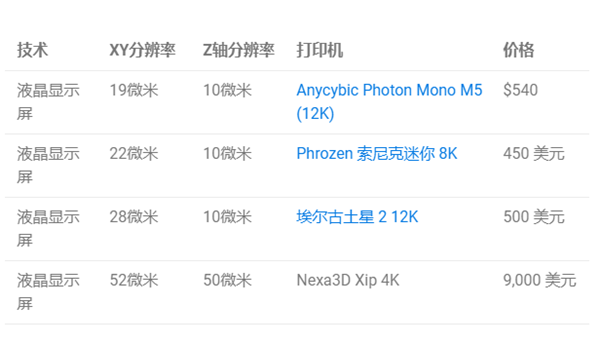
Use the pixel dimensions ofThe 19 micron Anycubic Photon Mono M5 allows you to obtain fine details on this model (Source: Anycubic)
The battle of 6K, 8K and 12K resolutions
buy an lcd monitorWhen it comes to resin (LCD) 3D printers (also known as mask stereolithography or MSLA), you’ll see ads for 6K resolution or 12K resolution. But what does this mean?
Let’s first see how an LCD printer works.The LCD screen uses a series of UV LEDs as a light source, which are projected onto an LCD screen (as shown in the image below). The LCD screen acts like a mask, allowing only certain areas of light to pass through. The light passing through it is shaped like a horizontal slice of the 3D model and solidifies the resin on the build area in this shape. This build zone is then moved up one layer to stop further curing of the polymer before the flash cure of the next 2D layer to the first layer. Finally, after several layers, the 3D object is formed.

replaceLCD screen on a Zortrax Inkspire resin 3D printer, recommended for replacement after approximately 200 hours of operation (Source: Zortrax)
ForFor LCD displays, the pixel density of the screen (that is, the number of small squares of pixels there are on an inch of screen) is the most important factor in horizontal resolution of a print.The pixel density of the LCD screen divided by the screen area is the printer resolution, also called pixel size. Contrary to what you may see in 3D printer marketing materials, resolution is not measured in the number of pixels on an LCD screen, like 4K, 6K, or 8K.
For example,The Phrozen Sonic Mega 8K’s LCD screen measures 7,700 pixels wide and 4,300 pixels deep. (The 8K in the name comes from the fact that the LCD screen is almost 8,000 pixels wide.) To determine the pixel resolution, you need to know the actual size of the LCD screen, because just knowing how many pixels there are across it doesn’t say. you don’t have anything about the resolution. Pixels are not a consistent unit of measurement. If you align 7700 pixels on a 100mm wide screen, your pixels will be smaller than if you align 7700 pixels on a 200mm wide screen.
This is why buyersThis is why the claim of “superb 11520 x 5120 resolution” is so frustrating.
The Phrozen Sonic Mega 8K has a pixel size of 0.043 mm, which can also be expressed in horizontal resolution of 0.043 mm or 43 micrometers (μm). For comparison, the Anycubic Photon Mono This means a horizontal resolution of 34 microns, which is higher than the resolution of Mega 8K. Large LCD printers, like the Mega 8K with a print volume of 330 x 185 x 400 mm, generally have a lower resolution than smaller LCD printers, like the Mono X 6K (197 x 122 x 245 mm).
SO,4K, 6K or 8K does not indicate the resolution. Instead, look at pixel size, which is usually listed as resolution and expressed as a number, such as 22 microns.
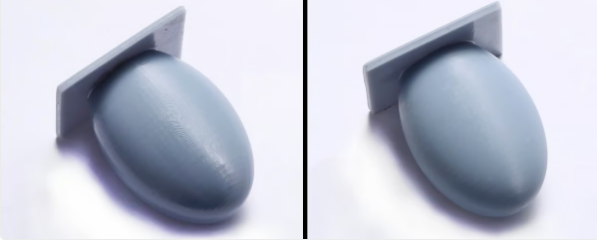
existThe same surface model printed on Anycubic Photon has the same layer height and resolution, but the model on the right has antialiasing enabled, softening the appearance of the layer lines (Source: Anycubic)
learnAnti-aliasing in 3D printing
throughThe light rays of the LCD screen are square, and combined with the height of the ground, they form a cube (or almost). The effect on the physical model is a surface that appears to be made of miniature Lego bricks. However, most parts look much smoother than this, why? For high-resolution 3D printers, the cubes (also called voxels) are so small that they are almost impossible to see with the naked eye, but there is another technique at play, antialiasing, which is a feature of the software cutting of the printer. .
Antialiasing is used in digital photography, computer graphics, and other applications to smooth the edges of any media composed of pixels. existIn 3D printing, the problem is controlling the amount or type of light that hits the resin voxels. If the light is not at full power, the voxels will not become fully solidified cubes, but rather semi-circular solidified elliptical voxels. If the edges of fully solidified voxels are like stairs, then antialiasing is like placing pillows on each staircase to give the appearance of a slideshow.
In slicing software, you can control the amount of antialiasing (also called grayscale) and associated metrics such as blur, i.e. how much of the outer layer will be affected by grayscale . Too much antialiasing and blurring and your prints will lose detail. If done right, antialiasing and blurring (or pixel processing tools) can make your prints look better overall visually and appear to have higher resolution.
Antialiasing and blurring are also used with other resin techniques, such asDLP and SLA.
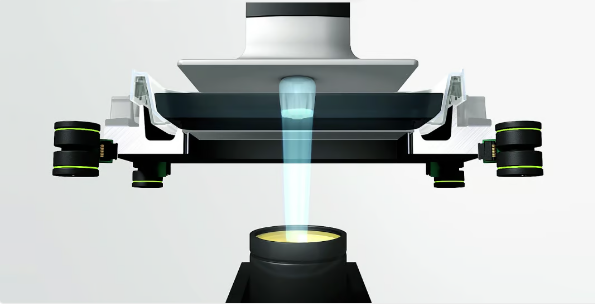
The inner workings of 3D printing technology are called digital light processing (DLP), which uses a projector to project a cross-section of a digital model onto a layer of resin (Source: Asiga)
digital light processing(DLP) is similar to LCD, but instead of using a screen through which light passes or is blocked, it uses a high-resolution light projector (sometimes called a “light engine”) to project light. light on a layer of resin. The light engine uses mirrors, lenses and, most importantly, digital micromirror devices (DMDs) on microchips to project UV light patterns in the form of slices or cross-sections of the 3D model.
You may be familiar with projectors used in movie theaters or officesDLP projection technology.
DLP in 3D printing uses DMD, which are tiny mirrors that can direct light onto the resin or direct it to the side and away. Each square mirror represents a pixel in the projected image.
Currently, professionallyIn a DLP 3D printer, you will see a 1920 x 1080 pixel DMD chip, which may also be called Full HD 1080p or 2K (because the pixel count is almost 2000). In some consumer machines, you’ll find 1280 × 720 pixel DMD chips. By the way, you may have heard that DMD maker Texas Instruments was planning to release a 4K chip last year. Unfortunately, the company had to cancel the expected mass production of this DMD, but a new version is expected to launch in early 2024. This means that we could see higher resolution DLP 3D printers (or, more likely, DLP 3D printers Larger DLPs) become available in 2024.

These lattice structuresThe 3D printed bicycle saddle produced for bicycle brand Specialized using a Carbon 3D printer is an example of DLP resin technology (Source: Carbon)
The density of the mirror array (or chip) is the main factor that determines print resolution, but the distance between the projector and the resin must also be considered.
most desktop computersDLP 3D printers have a fixed XY resolution (between 35 and 100 microns), but some allow you to adjust the projection distance between the light engine and the resin layer. This distance, like using a flashlight to create shadows on a wall, affects the level of detail that can be achieved.
Light reflected from the DMD’s mirrors passes through the projection optics, helping to focus the light and form a beam. Since mirrors direct light only where it is needed, DLP can produce sharper edges than LCD. With LCD screens, tiny amounts of light can escape through the edges of the screen’s obscured pixels, and the screen can never block 100% of the light.
DLP printers also have a higher light intensity (up to 16 watts) than the light sources of most LCD printers, and some DLP printers allow you to adjust the light intensity.
Although very precise, light in square pixels produces jagged edges, while curved edges should be what are called steps.This situation also exists in LCD printers. Smaller objects will have fewer problems on stairs, but larger rooms may have visible voxel edges.
The sharper the edges, the higher the resolution? Not necessarily, but the sharper the stairs, the more likely you are to manipulate the pixels using antialiasing, blurring, and another technique called pixel shifting to create a seemingly higher-resolution, more refined representation of features and images. outlines. In fact, some printer manufacturers claim printing resolutions that are half the size of their pixels.
How is this possible? what is4K and 8K DLP printers? To answer this question you need to understand pixel shift.
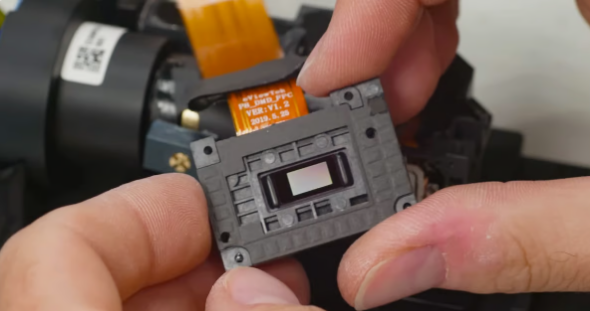
The DMD chip inside the light engine of the Anycubic Photon D2 DLP 3D printer (Source: Zach Freedman via YouTube)
learnPixel Shift in 3D Printing
Unlike antialiasing, pixel shifting (also called pixel scaling, extended pixel resolution, and extended pixel resolution orXPR) is not purely a software feature, it is also a mechanical feature. This is why DLP printers equipped with 2K DMD chips can claim to have 4K or 6K resolution. It is also used in other media that you may be familiar with, such as digital cameras, which offer a higher resolution mode than the camera.
By moving slightly between each layerAt the location of the DMD, a single layer is gradually exposed to multiple light exposures. This allows the light to fully cure areas of the pixel that have been exposed to long periods of light (e.g. 8 seconds) and partially cure areas of the pixel that have received less light.
You’ll see that this is often called sub-pixel resolution, while the actual resolution in pixels is called native resolution. Some printers allow you to select a native or sub-pixel resolution for each print job. This technique effectively increases the apparent resolution of the projected image by creating additional data points in each pixel.

DLP 3D printing technology is frequently used by dental professionals who demand high resolution and precision (Source: Asiga)
Using this bidirectional pixel shift we haveDPL printers with 2K DMD can claim to have 4K resolution. There is no true 4K DMD chipset in the 3D printing market yet, so the only way to get 4K or higher images is through pixel shifting.
For example,ETEC’s Extreme 8K DLP machine uses an electromechanical system that allows a small amount of tightly controlled movement at sub-pixel distances in its two 2K DMD chips (yes, there are two DMDs in this 3D printer), giving it provides 8K resolution. The Extreme 8K’s XY pixel size (pixel-adjusted) is 100 microns, which is higher than some LCDs, but it has a larger build volume (450 x 371 x 399 mm), which allows it to produce a very large section of image at very high resolution.
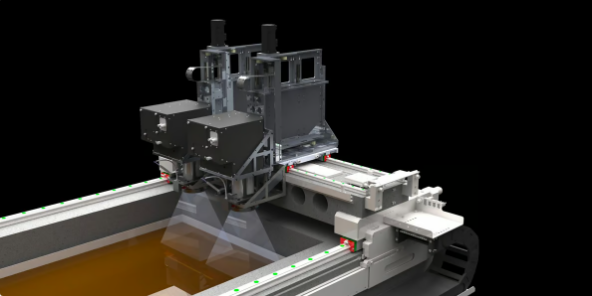
Light engine manufacturerIn-Vision has developed this 3D printer concept, using two or four DLP projectors on a gantry system, which can theoretically produce huge resin parts (Source: In-Vision)
Light engine manufacturerIn-Vision launched a DLP projector in 2021 that it says can produce 8K images because it can move pixels horizontally and vertically, but it has yet to be integrated into any commercial 3D printer.
Other professions and industriesDLP printers feature various pixel adjustment technologies, such as Movinglight from Prodways or Dynamic Exposure from In-Vision, in which the projector head moves over the building area while exposing the resin.

The Formlabs SLA 3D printer in action (Source: Formlabs)
stereolithography(SLA) is the new generation of resin 3D printer. It uses a laser to trace each layer of the part onto the surface of the resin body. Think of a laser as a flashlight, where the width of the beam determines the detail of the part. In laser technology, this is called the laser spot size, and it is one of the factors that determines the horizontal resolution of the SLA.
Another factor concerns the mechanism that controls the mirrors that guide the laser. These mirror galvanometers guide the laser to the correct coordinates, focusing the light upward through the bottom of the tank and hardening a layer of resin. As you can imagine, aA $200 SLA 3D printer has a more economical galvanometer setup than a $100,000 SLA 3D printer. The precision with which the laser is pointed plays an important role in the resolution.
XY resolution is once again the benchmark for SLA 3D printers. Resolution is a combination of the size of the laser spot and the increment by which the laser beam can be controlled. For example, the Formlabs Form 3 3D printer has an 85 micron spot size laser, but due to the constant line scanning process, the laser can move in smaller increments and the printer can print from parts consistently with an XY resolution of 25 microns.
This means that even if the laser spot size is larger thanThanks to the size of DLP pixels, laser machines with high-quality optics can also more accurately reproduce the surface of a part.
mostSLA 3D printers all have fixed lasers, but some, like the 3D Systems Dual Laser SLA 750 and Stratasys Neo series, have variable laser focus, such as 150 to 600 microns, allowing you to control where fine details are placed on this part. .

large resin3D printers such as the Stratasys Neo 450 tend to use SLA technology because the resolution is less dependent on the distance from the light source (Source: Stratasys)
So, which resin technology offers the highest resolution?
Pure numbers don’t tell the whole story, and it’s hard to say what resin3D printers make a linear technology comparison.Across the three resin technologies we just explored, price points vary significantly for the same resolution, underscoring the fact that print quality is more important than resolution.
When it comes to choosing a high-resolution resin printer, the differences between different manufacturers (consumer, professional and industrial) are more important than the differences between technologies. buy resin3D printers will take into account resolution as well as precision, speed, cost, material selection, etc.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.