While additive manufacturing continues to industrialize, post-processing has become increasingly important. This critical step allows users to improve parts to make them stronger, densest and even give them specific properties so that they can be used in important final applications. In different types of post-processing, for powdered bedsFor 3D printing (in particular metal), the most important thing is heat treatment. But what type of heat treatment is suitable for parts? How does it work? To answer these questions, we want to study two commonly used heat treatment processes: the thermal isostatic pressure (HIP) and the receipt.
Both are compatible with metal work, includingLPBF, EBM, powder link, DED and even nanoparticles jet. They can also be used with ceramics and polymers, although various degrees. The two methods have many advantages, including the strengthening of the material, which facilitates the treatment and improvement of its performance. Basically, the two technologies are used to optimize components, but the specific process and results are different.
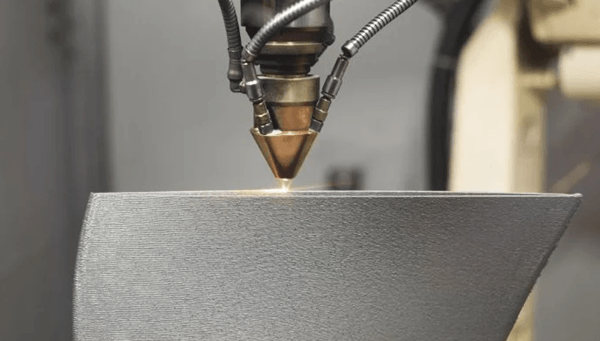
Printed metal parts (image source: industrial metal services)
Principle of thermal pressure and receipt
To understandThe differences and similarities between the hip and the receipt, we will examine each process. First of all, the receipt is a heat treatment which involves heating of metal, glass, ceramics or polymer and allowing the material to cool slowly to eliminate internal stress. This process modifies the physical properties of the material, sometimes also modifies the chemical properties, increases the ductility of the material, reduces the hardness of the material and facilitates treatment.
on the other hand,The hip consists in exposing parts to high temperatures and air pressure to eliminate the porosity of metallurgical materials. It can also increase the density of many ceramics, making a completely dense component.
Don’t forget,“I” in hip represents the balance. In this case, gas is applied equally, which means that it applies the same pressure in all directions of the material. This will lead to a creation of a uniform force around the object. Like the receipt, the hip can improve mechanical properties and the transformation of materials. The process can also assemble different materials to create unique parts.
Peak process
The receipt is carried out in an appropriate oven. These vary according to material requirements and costs, but can generally beHeat between 300 ° C and 1,000 ° C (for high -end models). The temperature inside the furnace must be carefully controlled, which is why these receipt ovens are often recommended – but note that any oven that reaches the correct temperature can theoretically be used if the temperature requirements are met.
The receipt is divided into three steps, which are all determined by temperature parameters depending on the type of material used. For Anneale, it is necessary to understand the material and its temperature needs.

Fucked frenace (image source:Thermcraft)
1. Recovery phase
In the first step of the receipt, that is to say the recovery stage, the temperature of the material rises to a level above the crystallization temperature, so that the atoms have the energy to move . The movement of atoms helps to redistribute and eliminate dislocations (irregularity in crystal structures), in particular in metals. This makes the metal more subject to deformation and therefore more ductile. Ceramics will also have the same effect, but to a lesser extent. Overall, this step helps reduce internal stress on the material.
2. Recrystallization steps
While the material continues to warm up, it ultimately reaches the recrystallization stage, which is high enough to allow recrystallization, but is still below the melting point. Currently, new stress -free grains are formed and developing, replacing the space left by the previous dislocation.
3. Grain growth step
Once the recrystallization is complete, the object begins to cool down and enters the stage of grain growth. As new particles are starting to develop and develop as they cool. However, the growth of these grains is not random. It is controlled according to the cooling speed and the atmosphere of the object cooling.
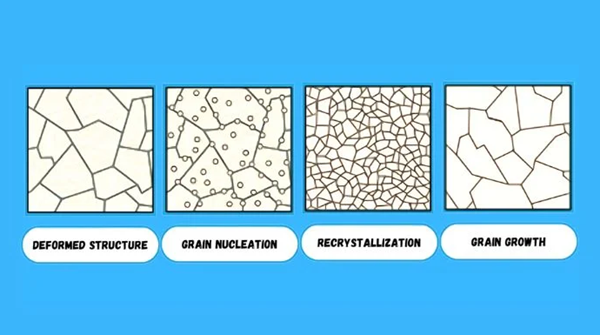
Graphic representation of molecular changes during the receipt (image source:Mechdaily)
Depending on the material, the receipt can take from four hours to a full day. It should also be noted that there are several types of receipts. Although it is not an exhaustive list of all of the receipt processes, some of the most commonly used processes are complete receipt, isothermal receipt, spheroid receipt, diffusion receipt and recupement of relief stress.
Parts manufactured by additive manufacturing, or at least parts in appropriate materials, can benefit from all these processes. If you have to choose between different types of receipt process, materials and application will be the decisive factors.
Thermal isostatic pressing process
The hip involves loading parts in high pressure confinement and exposing them to high temperature gases and high isostatic gases. The temperature can reach 2000 ℃ and the pressure can reach 310 MPa, which is approximately equivalent to pressure at 11,000 meters deep in the Mariana trench in the Pacific Ocean. The material then shrinks, retaining its original shape until the pores inside disappear, thus making the piece dense. This process is widely used to reduce constraints in sintering, casting and additive manufacturing components.
Argon is the most used pressure gas in this process. Argon is an inert gas that does not cause any chemical reaction in the material. The type of metal used can also minimize the impact of chemical reactions. Some systems also use additional air pumps to reach the necessary pressure levels. These gases are also applied to the object and maintained for a period of time.
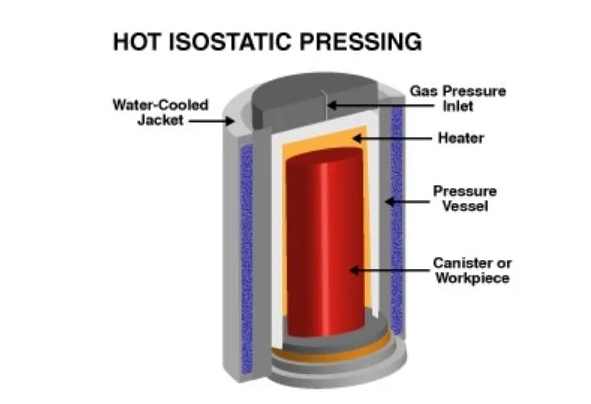
Image source: Federation of the metal powder industry
The temperature of the gas and the pressure level and the duration of the cycle all depend on the type of material used and the desired characteristics of the final product. The cycle can last from eight to twelve hours or days. This process gives parts a uniform microstructure, thus improving their performance.
Talk aboutHiperbaric, a leader in the field of 3D printing technology, isostatic thermal pressing, noted that the hip can be easily combined with the fusion of laser powder and EBM to obtain better quality parts. The powder bond, mangy, metal extrusion and metal spraying (such as pulverization of nanoparticles) are also compatible.
Compatibility of materials for thermal pressure and receipt
We have briefly mentioned above, but in terms of equipment,The hip and receipt processes overlap. In fact, they can be used with different metals, whatever the type.
Take the receipt as an example. This post-processing method is suitable for amorphous and crystalline materials. Therefore, it can be used in refractory metals, alloys and steels. Stainless steel is considered to be one of the most commonly used materials for parts, but bronze, aluminum, copper and brass are also mentioned. existOn the hip side, all metals seem compatible. It can even be used in difficult to process materials such as high temperature alloys based on nickel and titanium alloys.

Example of high temperature alloy based on nickel printed in 3D (image source: ally / Aubert & Duval)
However, metal is not the only compatible material. Ceramic components can also be adoptedHip or receipt for post-processing. Again, all ceramics seem compatible with the two processes as long as the properties of the material are respected.
The receipt, on the other hand, is characterized by compatibility with most polymers. Since it does not imply pressure but rather temperature changes, many polymers used in additive manufacturing can be recovered. For example, it is generally used to improveForce of ABS components. Other standard materials that do not have the best performance, such as PLA and PETG components, are more and more recovered, even the manufacturers. But for the hip, this is not necessarily the case.
Advantages and disadvantages of the process
Although receipt andThe hip involves different processes, but their advantages are similar. The two improve ductility and eliminate the defects of the material, whether pores (hip) or dislocations (receipt) in crystalline structures. Recuity and thermal isostatic pressure essentially eliminates internal defects and constraints and improves the uniformity of the microstructure and the properties of the materials. The two processes also help to consolidate the steps, as many 3D printed metal parts in any case require heat treatment to reduce residual thermal stress.
The receipt causes the migration of molecules in the microstructure, eliminating all the constraints that can be introduced during the formation of materials. This process also helps prevent cracks and improve the processor. In addition, due to the correction of dislocations in the metal network, conductivity is improved and the magnetic properties are improved. The receipt can precisely handle the material to obtain the desired properties by heating and selectively cooling the material, thus obtaining the desired type of grain and affecting the physical properties of the material.
The hip process can increase the density of the material because it forms metallurgical bonds between different diffusion materials. These improvements are essential for applications requiring strong resistance and reliability. This method can also repair material defects. For example, metal parts with holes inside can be treated to fill the compressed material holes. Overall, the thermal isostatic pressure and the REPUIT help reduce material waste as they improve existing materials, ensure their lifespan and reduce the need to buy new materials.
The materials undergoSchematic diagrams before and after the treatment of the hip (image source: hot isostatic x -ray tomography in the manufacture of metallic additive reveals the details of the closure of pores, direct science, a.du plessis ab, E. Macdonald)
The drawback of the two methods is the time necessary to complete the process. They may need to exceed24 hours, especially the hip, can take several days. Of course, these two technologies also require additional costs. They require initial costs for equipment and qualified operators, then require a lot of energy to warm up. The receipt can also involve forced cooling, which means that more energy is necessary. For both methods, the duration and the cost depends strongly on the materials used and the production scale.
Finally, the two processes affect the final dimensions of the part, which is not necessarily a drawback, but must be taken into account. RECUIT causes dimensional changes because the microstructure of the material changes, which isThis also happens in the hip process because the material is compressed. The degree of modification depends on factors such as the materials and the process parameters used.
Finally, when should the reception or the thermal isostatic pressure be avoided? If your parts do not need to improve mechanical properties, these processes may not be worth money. If your room has an internal cavity or a complex channel (which can collapse under pressure),The hip can be particularly unsuitable. The hip process is ideal when you want the parts to be dense. If you already have fully dense 3D printed parts (such as high quality parts made with a laser powder fusion), you don’t need to use this process.
ISOSTATIC REPUIT APPLICATION
Technically, the reception and the thermal isostatic pressure can be used in all areas where the properties of the materials are evaluated. However, it should be mentioned that although the thermal isostatic pressure is relatively difficult to achieve, except at the industrial level, the receipt can be carried out more easily, thus opening a wider audience.
However, in specific fields, these post-processing methods are widely used. For example,The hip was first used in the commercial environment of the aerospace industry. More specifically, it is used to produce turbine blades in a jet motor. Of course, these are not parts made thanks to additive manufacturing at the time.

3D printed turbine paces (image source: Siemens)
If we pay special attentionThe combination of hip and 3D printing, we will think of the medical field, and these two processes make it possible to make the hip and knee prostheses possible with titanium alloys. In the aerospace field, high temperature alloys based on nickel are used in turbine blades with LBPF and in fuel injectors with COCR. The hip is also used in the automotive field because it can increase confidence in 3D printed parts.
The receipt is common in similar industries because it can improve ductility, eliminate stress and reduce the hardness of the material. While improving magnetic properties, it can also reduce the fragility of metal. Therefore, the applications that benefit from these characteristics are the most appropriate.
The main receipt industries are medical, aerospace, automotive and semiconductor equipment. In the aerospace field, it is commonly used in aircraft components and can also be used in body panels in the automotive manufacturing industry. In the field of medicine, it can be used in medical devices such as orthopedic implants, because it can form alloys and metals biocompatible with the desired strength and durability. Finally, as the receipt can improve conductivity, it can be used to make semiconductors or solar cells in the electronics.
Manufacturer and price
A receipt is not necessarily necessary for annual parts. Sometimes a standard oven (like a laboratory oven) is suitable, in particular for small scales which do not require very high precision orDIY projects (mainly for polymers). However, if that is the case, a specialized reception furnace can be essential. The manufacturers of these devices include precons, Gasbarre Products, Inc and CM Furnaces, Inc.

Fucked frenace (image source:Precise)
Unlike the receipt,The hip requires specialized machines. You can hire a service or consider buying a machine yourself. The main manufacturers include Bodycot, Kobe Steel, Aalberts, Quintus and Esppi.
RECOIVE ANDThe cost of hip treatment depends on a number of factors such as the materials used, the magnitude of production, applications requirements and if you want to outsource the service or manage it internally.
For the receipt, the cost of a laboratory furnace is approximatelyFor $ 500, the cost of an industrial reception, varies from $ 3,000 to $ 100,000. The price range of thermal isostatic presses is similar: small solutions start at around $ 7,000, while large solutions can cost hundreds of thousands or more.
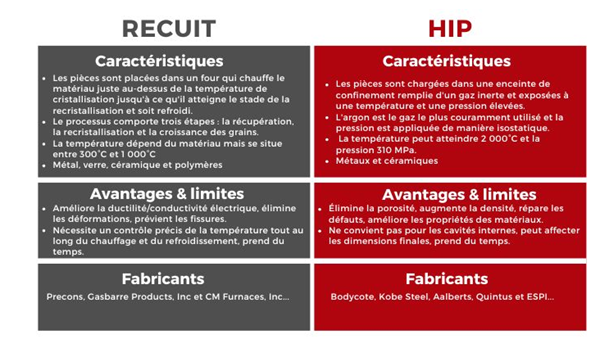
Image source:3DNATIONS
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.