Today we share some basic mechanical design knowledge, hoping to help everyone.
1. Failure modes of mechanical parts: overall failure, excessive residual deformation, surface damage of parts (corrosion, wear and contact fatigue), failure caused by damage to normal working conditions.
2. Requirements that the design parts must meet: requirements to avoid failures during the predetermined life period (strength, rigidity, service life), structural process requirements, economic requirements, low mass requirements and reliability requirements .
3. Part design criteria: strength criteria, rigidity criteria, lifespan criteria, vibrational stability criteria and reliability criteria.
4. Part design methods: theoretical design, empirical design and model test design.
5. Commonly used materials for mechanical parts: metal materials, polymer materials, ceramic materials and composite materials.
6. The strength of parts is divided into: resistance to static stress and resistance to variable stress.
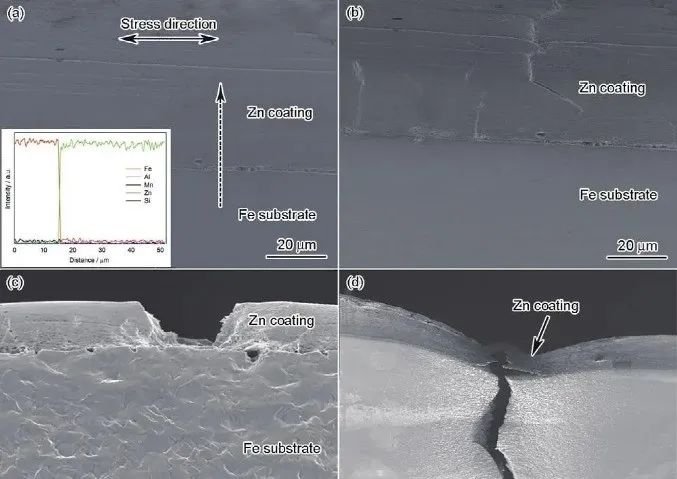
7. Stress ratio: r = -1 is a symmetrical cyclic stress; r = 0 is a pulsed cyclic stress.
8. Stage BC is strain fatigue (low cycle fatigue): CD is finite life fatigue stage; the line segment after point D represents the infinite life fatigue stage of the specimen; point D is the limit of lasting fatigue.
9. Measures to improve the fatigue resistance of parts: minimize the impact of stress concentration on parts (load relief grooves, open annular grooves), select materials with high fatigue resistance and specify heat treatment methods and strengthening processes that can improve fatigue resistance. of materials.
10. Sliding friction: dry friction, boundary friction, fluid friction and mixed friction.
11. The wear process of parts: running-in stage, stable wear stage, severe wear stage; we should strive to shorten the break-in period, prolong the stable wear period, and delay the arrival of severe wear.


12. Classification of wear: adhesive wear, abrasive wear, fatigue wear, erosion wear, corrosion wear and friction wear.
13. Lubricants are divided into four types: gaseous, liquid, solid and semi-solid; Greases are divided into: calcium-based grease, nano-based grease, lithium-based grease and aluminum-based grease.
14. Ordinary connection threads have an equilateral triangular shape and good self-locking properties; rectangular transmission threads have higher transmission efficiency than other trapezoidal transmission threads;
15. Commonly used connection threads require self-locking, so single-threaded threads are often used; Transmission threads require high transmission efficiency, so double or triple threads are often used.
16. Ordinary bolt connections (connected parts have through holes or reamed holes), double-headed stud connections, screw connections and set screw connections.
17. The purpose of pre-tightening threaded connections: to improve the reliability and tightness of the connection and to avoid gaps or relative slippage between the connected parts after being loaded. The basic problem with loosening threaded connections is to prevent the pairs of spirals from rotating relative to each other when loaded. (Anti-loosening by friction, anti-loosening mechanically, anti-loosening by destruction of the relationship between the movement of the pair of spirals)
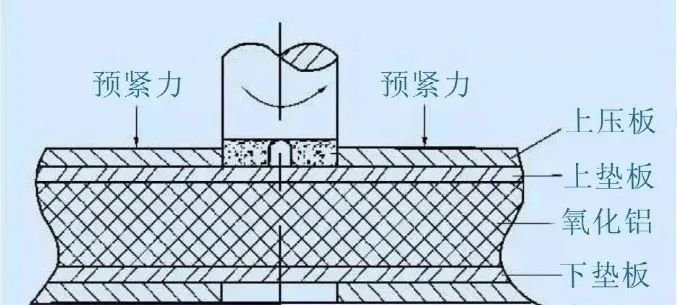

18. Measures to improve the strength of threaded assemblies: reduce the stress amplitude that affects the fatigue resistance of bolts (reduce the stiffness of the bolt or increase the stiffness of the connected parts), improve the uneven distribution of loads on the threads , reduce the impact of stress concentration and adopt reasonable manufacturing process.
19. Types of key connection: flat key connection (both sides are working surfaces), semi-circular key connection, wedge key connection, tangential key connection.
20. Belt transmission is divided into: friction type and mesh type.
21. Instantaneous maximum belt stress occurs when the tight edge of the belt begins to wrap around the small pulley; the stress changes four times during one revolution of the belt.
22. V-belt transmission tensioning: regular tensioning device, automatic tensioning device, tensioning wheel tensioning device.
23. The number of links of the roller chain is generally an even number (the number of teeth of the sprocket is an odd number). When the roller chain has an odd number, an excessive number of links are used.
24. The purpose of chain drive tension: to avoid poor meshing and vibration of the chain when the free edge of the chain sags too much, and to increase the meshing angle between the chain and the pinion.
25. Gear failure modes: gear tooth breakage, tooth surface wear (open gears), tooth surface pitting (closed gears), tooth surface sticking, plastic deformation (ridges on gear driving wheel, grooves on the driving wheel).
26. Gears with working surface hardness greater than 350HBS or 38HRS are called hard face gears; otherwise, they are soft-faced gears.
27. Improving manufacturing precision, reducing gear diameter to reduce circumferential speed, can reduce dynamic load; In order to reduce the dynamic load, the gear can be cut in order to give the gear teeth a drum shape and improve the tooth tip. directional load distribution.
28. The larger the diameter coefficient attack angle, the higher the efficiency and the worse the self-locking property.
29. Move the worm gear. After moving, the index circle and the pitch circle of the worm gear still coincide, but the pitch line of the worm has changed and no longer coincides with its index circle.
30. Worm transmission failure modes: pitting corrosion, tooth root fracture, tooth surface sticking and excessive failure often occur on worm gears;
31. Power loss of closed worm drive: loss of mesh wear, loss of bearing wear, loss of oil splash as parts entering the oil pool stir the oil .
32. The worm drive should perform heat balance calculations based on the condition that the heat generated per unit time is equal to the heat dissipation in the same time. Measures: install heat sinks and increase the heat dissipation area, install fans at the end. the worm shaft to accelerate the air flow and install circulating cooling pipelines are installed inside the box.
33. Conditions for the formation of hydrodynamic lubrication: the two relative sliding surfaces must form a converging wedge-shaped space; the two surfaces separated by the oil film must have sufficient relative sliding speed and their movement must cause the lubricating oil to flow from the large opening into the small opening; lubrication. The oil must have a certain viscosity and the oil supply must be sufficient.
34. The basic structure of bearings: inner ring, outer ring, hydraulic body and cage.
35. 3 tapered roller bearings, 5 thrust ball bearings, 6 deep groove ball bearings, 7 angular contact bearings, N cylindrical roller bearings 00, 01, 02, 03 respectively d=10mm, 12mm, 15mm, 17mm 04 means d = 20mm, 12 means d = 60mm.
36. Basic rated life: The number of rotational speeds or hours of operation at which 10% of the bearings in a bearing group suffer from pitting corrosion damage, and of which 90% do not suffer from pitting corrosion damage. damage caused by pitting corrosion, is considered the service life. of the bearing.
37. Basic dynamic load: The load that the bearing can support when the basic rated life of the bearing is exactly 106 revolutions.
38. Bearing configuration method: each of the two fulcrums is fixed in one direction, one point is fixed in two directions, the other fulcrum is free to move, and the two ends are supported by free movement .
39. Bearings are divided according to load: rotating shaft (bending moment and torque), spindle (bending moment) and drive shaft (torque).
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.



















