High Resolution 3D Printer (2): Highest resolution FDM 3D printer
High resolution 3D printer (3): The highest resolution resin 3D printer
talk aboutWith 3D printing, talking about resolution is a bit like talking about car performance: it’s relative, it can be subjective, and it covers a range of possible measurements.
For some, high resolution means fine details, while for others it means a smooth surface finish. You can also think of high resolution as a measure of overall print quality. To make this topic even more confusing,The word “resolution” is often used interchangeably with precision or accuracy, even by printer manufacturers.
There are certain resolution standards, according to whichType of 3D printer (filament, resin, powder, etc.), but be aware that the highest in terms of resolution is not always the easy answer. Today, Mohou.com will discuss it in depth with you.


A,Different ways to measure resolution
High resolution is stereolithographyResin resolution is the most commonly mentioned parameter in resin technologies such as (SLA), digital light processing (DLP), and liquid crystal display (LCD), which is why a large part of this guide covers resin resolution.
for resinFor 3D printers, resolution is typically given in horizontal (XY) measurements, while for fused deposition modeling (FDM) and powder bed technologies, resolution is typically given in vertical (Z) measurements or simply in layer height.
Regardless of how you interpret resolution, it generally refers toThe smallest artifact that a 3D printer can create in a controllable and repeatable way. In some cases, printer manufacturers will state a “theoretical” resolution that they are certain their machines can achieve, but for resolution to be a useful quality, it must reflect something practical and predictable.


This is provided by the printing serviceA detailed dragon resin 3D print made by Merit3D shows some layer lines that can be smoothed out with post-processing (Source: Merit3D)
When we talk about resolution, we usually mean horizontal or vertical resolution, or both, depending on3D printer technology. Horizontal resolution is the smallest possible detail that a printer can print on a flat surface. On the other hand, vertical resolution or layer height is the minimum height of a layer that can be printed. This may seem simple, but there are still some nuances, which we will detail below.
Resolution is often confused or used interchangeably with the following terms, which are also important but do not fit with how we define resolution.
Minimum feature sizeIt is the smallest visible entity that can be embedded or projected from a surface. It is related to resolution, but is usually slightly larger since it is a visual property.
PrecisionGenerally withMeasured by the degree to which a 3D printer deviates from a target resolution, such as the accuracy of aiming a dart. For example, 2 microns accuracy means the print can be off target by 2 microns in any direction. An accuracy of ±20 microns may be acceptable for one application but not for another.
Precisionis a general term that usually includes layer height, precision, resolution, and other factors. It is not a numerical measurement of any specific print property. High precision is a common requirement among manufacturers.
“tolerance”is your professional and industrialOne word you will see in the description of a 3D printer: it is essential that the printed parts can be produced to the required specifications and exact dimensions. Much like precision, a 3D printer’s tolerance is not a numerical measure of a specific printing property, but it can be equated to precision. If your part specifications require a 2mm tolerance and your printer has an accuracy of 0.5mm, you can count on it to achieve the required 2mm tolerance.
3D printer manufacturers may use different terms to refer to the same quality and may not even disclose certain measurements, such as layer height or resolution.
In the absence of any industry standard for data sheets, manufacturers aim to interpret the attributes of their machines in a way that brings out their best functionality. Additionally, and more importantly,There are thousands of them on the marketWith 3D printers, it’s not important to compare spec sheets, it’s important to consider your application, budget, timeline, materials, and other factors.
However,Resolution in 3D printing is shrouded in mystery, so we want to clarify what it actually means.
two,Resolution of 3D printing technology


The height or resolution of the layer isA measure of the resolution of the 3D printer, but it is also adjustable and depends on the material
(Source: Eco3D Designs, CEAD)
How resolution is measured varies depending on the technology, but here are some of the main ones described3D printing technologies ranked by resolution (from smallest to largest).

three,unique miniature3D printing

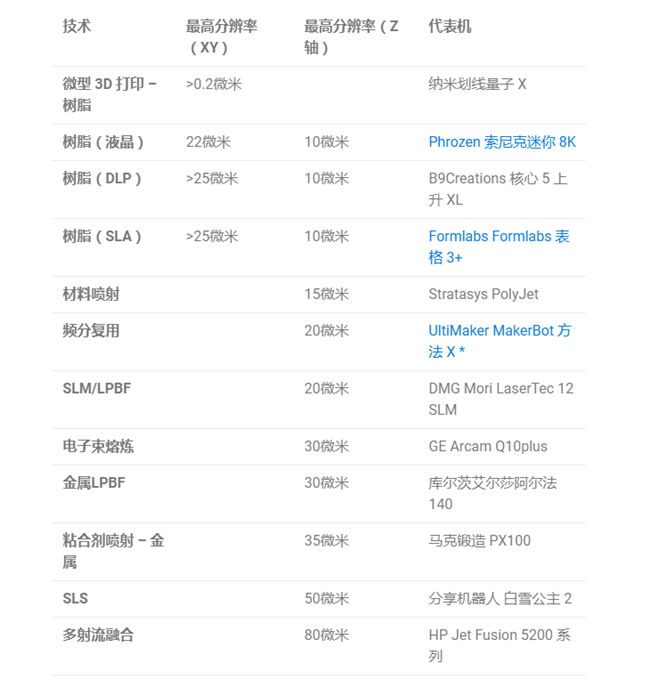
Ultra-high resolution micro-3D printing from Nano Dimension Fabrica Group (Source: Nano Dimension)
Smallest resolution3D printers belong to the category of 3D micro-printing. The resolution here is about 20 nanometers, or 0.00002 millimeters, which is about 5,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair and about 5,000 times smaller than the resolution of a desktop 3D printer classic. This is definitely overkill if you’re looking for specific details on a product prototype.
miniature3D printers are commonly used in electronics for manufacturing chips. In fact, in 2023, the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore announced that it was working on developing a 3D printer for high-performance optical devices for AR/VR headsets, SLR cameras and smartphones, which does not require no 3D printing.
Used in medical devices such as cardiac stents and in very specialized precision manufacturing.
Four,Other factors affecting resolution
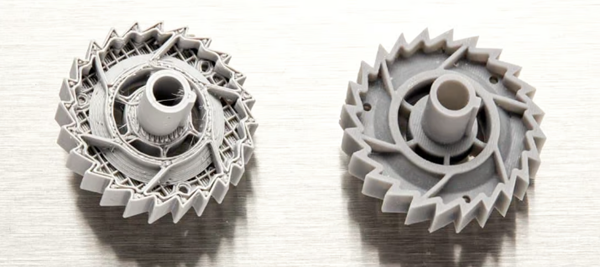

FDM 3D printing (left) cannot achieve the resolution and surface quality offered by SLA printing (Source: Formlabs)
The material you choose has the biggest impact on your resolution, here’s why3D printer manufacturers often offer different resolutions for each material they recommend. There are other factors that affect the resolution achieved with a 3D printer, including:
Material quality
Slicer Settings
Nozzle Size
Machinery vibrations
Parts are worn or defective
If yourIf your 3D printer is unable to reach the previous resolution, a possible cause is that part of the 3D printer has just worn out. DLP projectors can only maintain a stable high intensity for a certain number of hours (around 10,000) before needing to be replaced. LCD screens begin to deteriorate and burn out after around 1,000 hours of printing, while FDM printers require new nozzles after a period of use.
five,How important is resolution in 3D printing?


to useFormlabs Carbon Fiber Infused Nylon 11 Powder Material for SLS 3D Printing of Parts (Source: Formlabs)
Resin3D printer manufacturer Formlabs states in one of its excellent guides that “resolution itself is often just a vanity metric.”
The resolution itself is not specific to purchasing or not purchasingThe case with 3D printers, in fact, is that the industry’s obsession with resolution can be a barrier to adoption of 3D printers because resolutions are vague and often confusing, leading to consumer confusion.
resolution, combined with a series of other measurements, can produce“Quality” parts. Therefore, comparing data sheets can serve as a starting point for purchasing your printer, but should not be used as a basis for choosing a machine. Instead, start with the quality of the part you need, what it should look like, and how it should function.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.










